API Design-First Development: A Quality Engineer's Insight
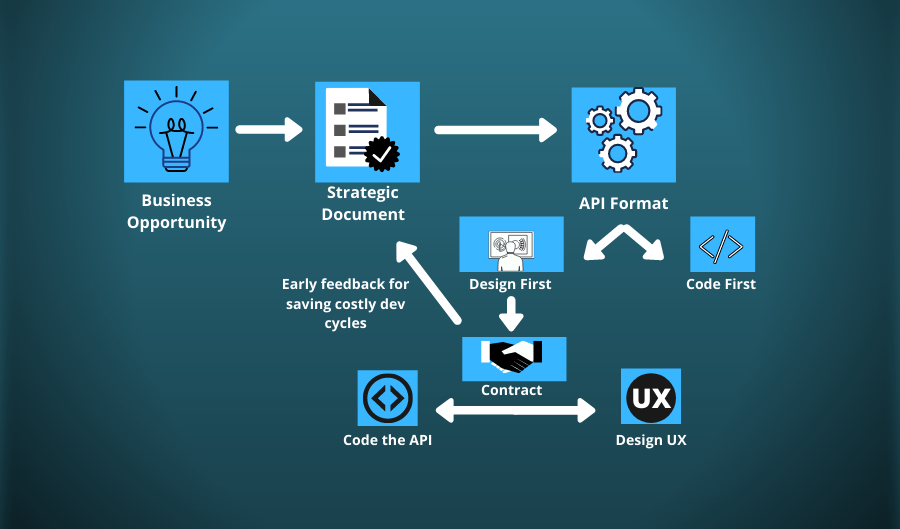
API design-driven development is an approach where the design and documentation of application programming interfaces (APIs) take precedence before implementing the rest of the software. It promotes collaboration, early validation, and reusability of APIs, making them a central building block in the development process. This approach ensures consistency, scalability, and adaptability in modern software development.
API design-first means you describe the API requirement in a human and machine-readable contract, such as an OpenAPI document —before you write any code.
How is it different from Code-First Approach?
In a code-first approach, developers write code first to build the application's functionality and then design the API later. This method can lead to less structured APIs and may require additional effort to ensure consistency and documentation. In contrast, API design-driven development prioritizes designing and documenting the API before writing the code, resulting in more organized, well-documented, and collaborative development.
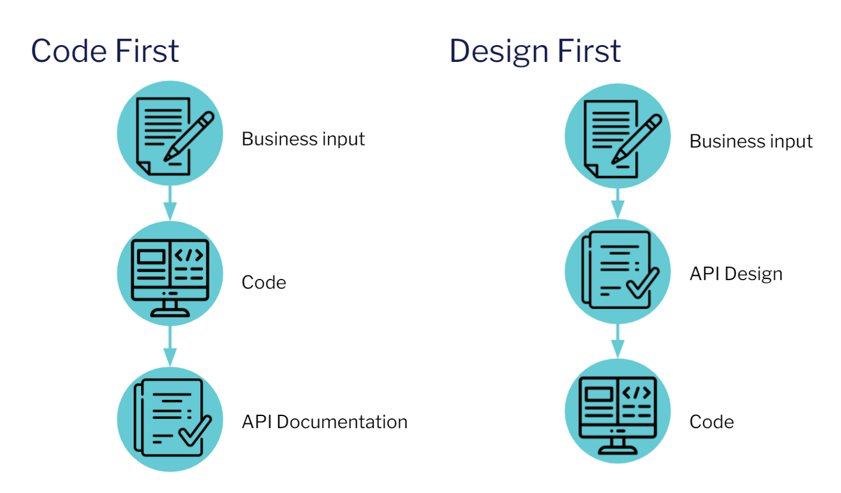
API design-driven development offers several key benefits:
- Inclusive Stakeholder Involvement: By involving all stakeholders in the API design process, it ensures that the needs and requirements of various teams, including developers, architects, and product managers, are taken into account from the outset. This collaborative approach leads to a more comprehensive and well-rounded API design.
- Consistent Communication: When every team follows the same API design, it creates a unified language for communication. This consistency extends to the tools and technologies used, making it easier to manage and collaborate across different parts of the project. It establishes a "single source of truth" for the project's API specifications.
- Parallel Development and Swift Feedback: With the API design serving as the foundation, development teams can work in parallel. Front-end and back-end teams can operate simultaneously, using mock APIs for the user interface, which shortens the feedback loop and accelerates the development process. This parallel workflow helps detect issues and resolve them early in the development cycle, reducing the risk of costly revisions later on.
Why opt for this approach? Let's delve into the advantages it offers.
Client Code Generation including models:
By designing APIs first, you can generate client code and models directly from the API specifications. This ensures that client applications are tightly integrated with the services and are less prone to compatibility issues.
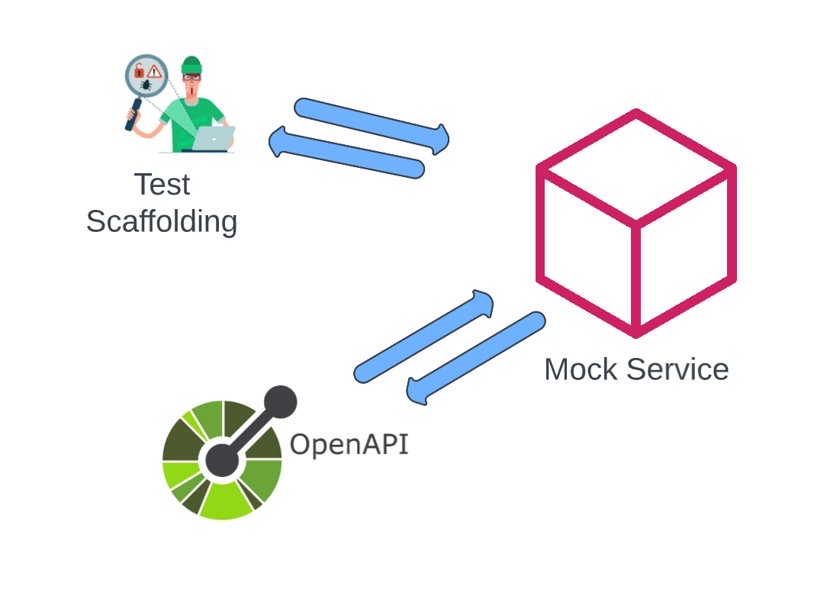
Test Scaffolding before service is built:
API design allows you to create test scaffolding even before the actual service implementation begins. This means that testing can commence early in the development process, identifying and rectifying potential issues at an early stage.
Mock Service Generation:
With well-documented API designs, it's easy to create mock services that mimic the expected behavior. These mock services can be used for testing, enabling frontend and backend teams to work in parallel, enhancing efficiency.
Familiar and collaborative API development:
A design-first approach ensures that all teams work with a common, collaborative API design. This reduces misunderstandings and promotes a cohesive development process.
Improved consistency and scalability:
API design-driven development enforces consistency in API structure and behavior, which is crucial for long-term scalability. The unified design reduces the likelihood of ad-hoc API changes that can lead to compatibility issues.
A reliable source of truth and standard for API testing:
The API design serves as the definitive source of truth for the project. It provides a standardized and documented foundation for API testing, making it easier to identify and address discrepancies or issues.
Postman Collection Generation:
With well-documented APIs, it's simpler to generate Postman collections for testing and development purposes. This further streamlines testing and collaboration with external teams or stakeholders.
What is Client Code Genetation?
- Tools such as OpenAPI Generator allows the generation of API client libraries (SDK generation), server stubs, documentation, and configuration automatically based on the API specs.
- Eliminates the need to write the boilerplate code necessary for calling the APIs
- Generated SDKs will closely match the API Structure.
- The generated HTTP client code or SDK can be used for both testing and development.
- Devs and QEs can leverage the same object models and generated client code.
- Test development is a lot faster using generated HTTP clients, models/schemas, etc.
What is Mock Service Generation?
- Generate mock service based on the API specification such as an OpenAPI spec or a GraphQL schema.
- Teams can work in tandem before the API is available through mock services.
- Mock internal and external APIs within your platform with dynamic responses.
- It helps accelerate the development of new APIs.
How does it help with Test Scaffolding and Testing?
- Start writing tests even before that actual service is built.
- The mock responses can be adjusted based on test requirements.
- It also enables schema validation where you can compare the virtual mocked service against the actual service for any gaps.
- Generate postman collections based on the OpenAPI specs.
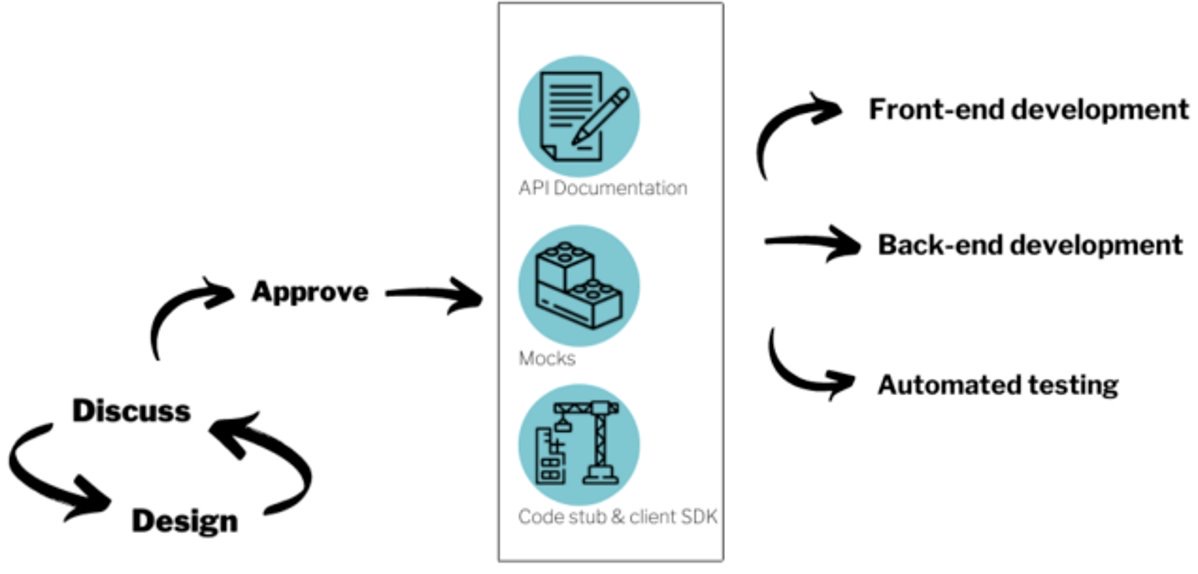
Documentation - Use it as a Single Source of truth
- Poor or non-existent documentation impacts the quality, cost, and speed of API development.
- Good documentation helps expands knowledge beyond the developers working on the APIs.
- It provides detailed documentation on what the API does and how to get started.
- It improves the developers’ quality engineers’ experience through collaboration and shared information.
How does it help with Increased collaboration?
- Helps collaborate more efficiently by parallelizing work around concrete technical contracts.
- Both QEs and Devs can leverage the generated models and schemas for consistency.
- Transparency — the teams impacted including QE will always know when a change has been made and the impact on testing.
- The development experience is greatly improved with multiple operations automated.
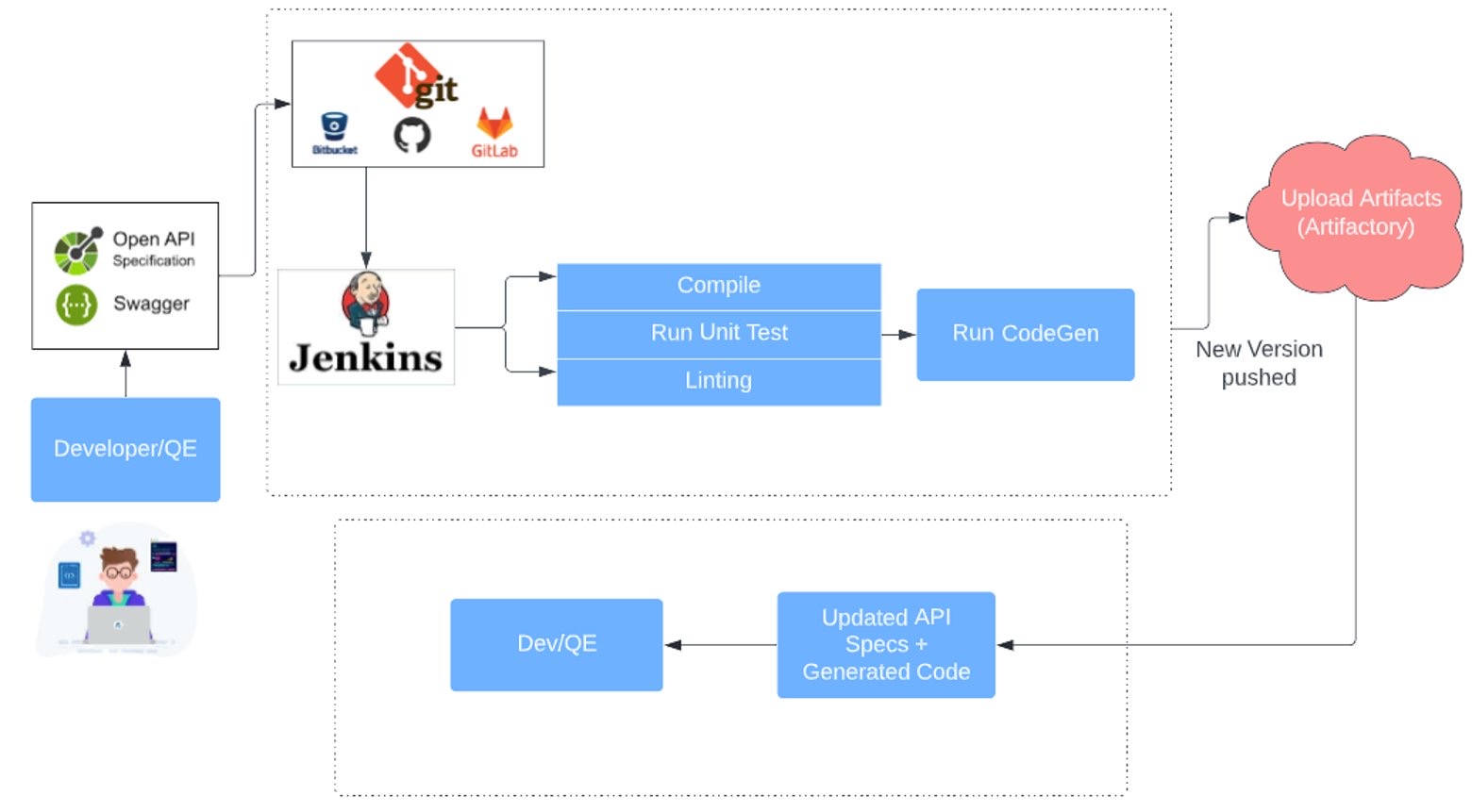
Automate the CodeGen process in the pipeline for better collaboration and consistency
Next Steps
- Learn more about OpenAPI Standards: https://swagger.io/specification/
- Learn more about OpenAPI CodeGen: https://github.com/OpenAPITools/openapi-generator
- Example of Mock server generator for Swagger and OpenAPI: https://github.com/stoplightio/prism
- Learn more about GraphQL Schema: https://www.telerik.com/blogs/graphql-schema-resolvers-type-system-schema-language-query-language
- Example of GraphQL CodeGen using Python: https://sgqlc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/

About Testingfly
Testingfly is my spot for sharing insights and experiences, with a primary focus on tools and technologies related to test automation and governance.
Comments
Want to give your thoughts or chat about more ideas? Feel free to leave a comment here.
Instead of authenticating the giscus application, you can also comment directly on GitHub.
Related Articles
Testing iFrames using Playwright
Automated testing has become an integral part of web application development. However, testing in Safari, Apple's web browser, presents unique challenges due to the browser's strict Same-Origin Policy (SOP), especially when dealing with iframes. In this article, we'll explore known issues related to Safari's SOP, discuss workarounds, and demonstrate how Playwright, a popular automation testing framework, supports automated testing in this context.

Overview of SiteCore for Beginners
Sitecore is a digital experience platform that combines content management, marketing automation, and eCommerce. It's an enterprise-level content management system (CMS) built on ASP.NET. Sitecore allows businesses to create, manage, and publish content across all channels using simple tools.
